
GROUND IMPROVEMENT ON THE BACK SIDE OF RETAINING COLUMNS CASE STUDY
Double packer grouting and water-stop reinforcement technology for gravel layer
1. Project Background
Ground Improvement : The newly constructed foundation for a hospital has a gravel layer mixed with layers of silt sand, and retaining columns with steel supports used as a retaining facility.
Need to prevent gravel from collapsing during the excavation process with ingress of surface water during rain and groundwater into the foundation through the stratum between retaining columns.
Water stop and reinforcement grouting between the retaining columns are planned to reduce the permeability coefficient of the stratum and increase the cohesion of the gravel layer.
―
2. Solution
High-pressure jet piles cannot be formed in the layer of gravel and silt, and any cement grout that escaped into the excavation face would solidify, it would have a serious impact on the progress of future foundation pit excavation. Careful evaluation by the company’s professional engineers and design unit experts was made.
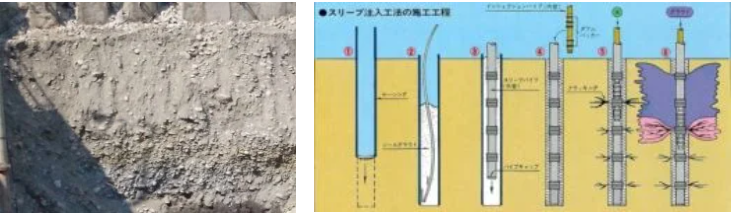
In view of the large area of the basement of this project and the long excavation time of the gravel layer, the decision was made to adopt Double Packer Grouting.
This method can be repeated, combined with slow-setting and long-acting sodium silicate chemical grout (SSA) for low-pressure grouting to achieve the water-stopping and reinforcement effect on the ground between the retaining columns during the excavation process.
In the event of localized stratum leakage due to construction factors or natural disasters, quick-setting grout can also be quickly supplemented to solve groundwater ingress hazard into the excavation face.
―
3. Works Design
The perimeter of the foundation pit of this project was about 327m, and the excavation depth was GL-13.9m. In order to be in line with economic considerations, the depth of ground improvement is only to be applied to a thick layer of silt sand between GL-11.0m and GL19.0m.
Due to the construction unit’s tight schedule, the grouting work was required to be completed within one month.
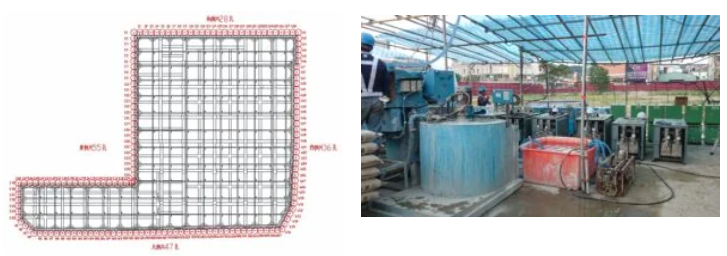
In order to meet the needs of the owners, the planning and design adopted was drilling imbedded pipes, grout material pouring, supplementary grouting by grouping, and dividing up operations.
The drilling crew first uses a large percussion drill to drill holes with a depth of GL±0m~GL-19m at the stakeout position with a hole spacing of 2m, and uses CB grout to bury and fix the Marshall pipes (sleeve pipes).
The grouting team uses an automatic monitoring grout machine to split open the side of the borehole with clean water to solidify the grout.Then according to the preset pouring volume of 25% porosity, using 6~12 L/min pouring rate, fill the voids with CB grout and 1-hour solidifying sodium silicate chemical grout, according to the volume of grout with 15% porosity and 10% porosity respectively.Carry out skip-hole pouring in gravel/silt layer.
For the supplementary grouting crew, the grouting flow and feedback pressure recorded are studied and evaluated.Then supplementary grouting is performed at locations where the voids are larger or the grouting material has missed, and the grouting pressure at each stage is not greater than the initial pressure of the grouting +50~200 kPa.
After grouting meets the grouting design requirements, randomly select hole positions and depth to conduct on-site water permeability tests to confirm that the formation permeability coefficient is not greater than 1×10-5cm/sec.

―
4. Works Process
The ground improvement works were performed before excavation, and although the scope of grouting was limited to the periphery of the foundation pit, the slow-setting chemical grout inevitably spread out, causing the amount of grout material to be higher than expected.
Fortunately, although the grout partially penetrated into the foundation, the compressive strength of the grout after curing is only about 400 kPa, which does not cause excessive influence on the excavation process.
In addition, in order to meet the owner’s request for completion within a limited time, the company used 14 grouting units and monitoring systems to perform grouting and supplementary operations at the same time, which greatly increased the works capacity.
During the works process, the company’s on-site engineers and site directors monitored the grouting status at any time and could revise it immediately.They also set inspection points during the time of material arrival, grout mixing and grouting completion, etc.
To ensure that the machinery, equipment, materials, and pouring process were in the best condition, and reduced the time use caused by repeated supplementing.

―
5. Results
This project used the Double Packer Grouting method to water-stop and reinforce the high-permeability stratum surrounding the foundation pit, which greatly improved the stability of the stratum between the retaining columns.
After all grouting work was completed, on-site permeation tests and excavation leakage inspections were carried out in accordance with the contract.
The inspection results are in full compliance with the design requirements.In the subsequent full excavation and basement construction process, no serious water seepage or sidewall collapse occurred, and the site improvement work on the back side of the retaining column was successfully completed.

―
Ground Improvement on The Back Side of Retaining Columns Case Study
將下載檔案寄至:
・More Construction Result Sharing
Contact us:+886 2769-2355
Copyright ©Jines Construction Co.,Ltd