
WATER INRUSH TREATMENT AND GROUND IMPROVEMENT AT THAILAND MRT STATION EXCAVATION
Water-stop and stabilization improvement of site damaged by ground uplifting
1. Project Background
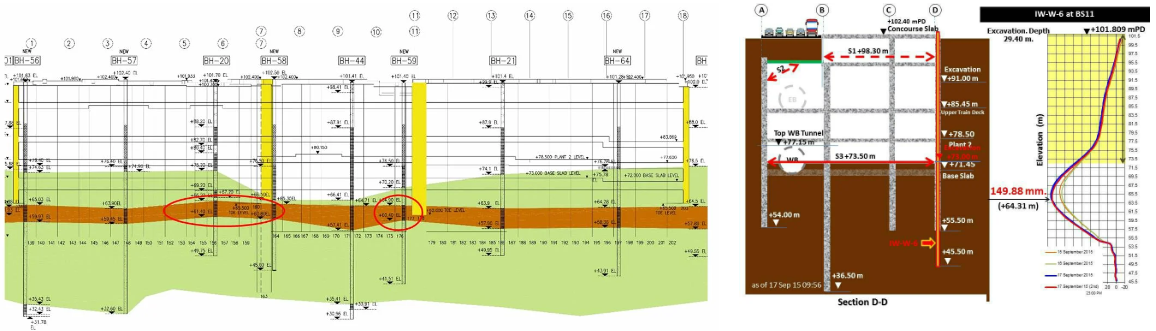
In a Thai MRT station construction project, the reverse construction method was employed, with diaphragm walls penetrating into the clay layer below the excavation level to prevent groundwater infiltration.
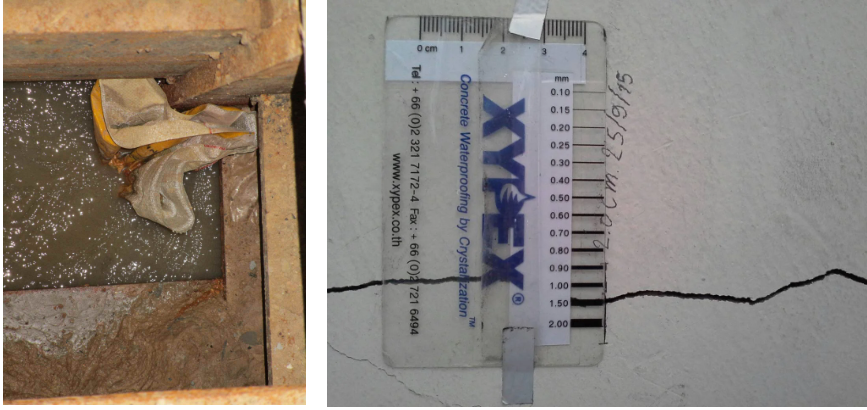
However, an unexpected and severe water and sand inrush occurred during the excavation process, leading to localized deformations of the diaphragm walls and surface subsidence.
According to the geological survey report, the underlying clay layer was found to be relatively thin and occasionally interspersed with a thin layer of sandy soil, indicating that the water inrush was likely caused by the upward heave of the clay layer under the pressure of the underlying sandy soil.
To prevent further escalation of the situation, the construction team promptly filled the water outflow points with graded materials to prevent sand gushing out.
Additionally, they engaged professional contractors to develop an improvement plan and implement waterproofing reinforcement measures after thorough review and approval.

—
2. Solution
The excavation site consisted of a 5-meter-thick layer of sand below the excavation face, followed by a 4 to 7-meter-thick layer of clay, transitioning into a sandy layer.
The water inrush occurred close to the excavation face, where the clay layer is relatively thinner. The water flowed upward, with a discharge rate ranging from 300 to 700 cubic meters per hour.
Possible sources of groundwater were analyzed as follows:
(1) Upraising causing pressurized water to infiltrate beneath the clay layer(2) existing unsealed boreholes or pre-existing wells penetrating through the clay layer, and (3) flaws in the diaphragm walls between the excavation level and the clay layer, resulting in the inrush of surrounding groundwater. Considering that any of these factors individually or in combination could have contributed to the water inrush, the preferred approach in formulating the mitigation plan was to develop a solution that could simultaneously address all three potential water pathways.

—
3. Works Design
Considering factors such as site area, uncertain leakage points, construction time, and project budget, the water inrush treatment for this project will involve employing the overlapping encapsulation method around the suspected leakage points.
Moreover, to avoid the risk of significant water inrush by penetrating the clay layer, the grouting depth had to be limited to approximately 2m-3m above and below the clay layer.
The construction design was outlined as follows:
(1) Construction of temporary work structure platform above the leakage points;
(2) Utilization of a dual-pipe drilling method with adjustable grout setting time to penetrate into the clay layer by approximately 2m, recording the locations and depths of loose zones encountered during drilling;
(3) After reaching the intended grouting depth, initially sealing the borehole walls with quick-setting SSA chemical grout to prevent backflow;
(4) Adopting the reverse-grade injection method and injecting quick and slow-setting grouts. FLW cementitious chemical grout to be used for zones with loose formations, while the remaining areas are injected with SSA chemical grout;
(5) Injection continues until approximately 2m above the clay layer while adjusting the injection height or terminating the grouting based on the effectiveness of water sealing;
(6) Utilizing the overlap covering method to seal the water inrush. In cases where complete sealing is not achievable, appropriate adjustments to borehole positions or increased grouting quantities may be made after approval.

—
4. Works Process
Due to the use of the reverse construction method in this project, the locations of water outflow points appeared irregularly as the excavation depth increased. Consequently, construction personnel, machinery, and materials needed to be constantly on standby and available for grouting operations.
The temporary work structure platform also needed to be relocatable according to the shifting construction positions, either inside the underground area or on the framework structure at ground level.
This posed significant challenges for construction scheduling and site layout, requiring careful coordination and adaptability on-site.

—
5. Results
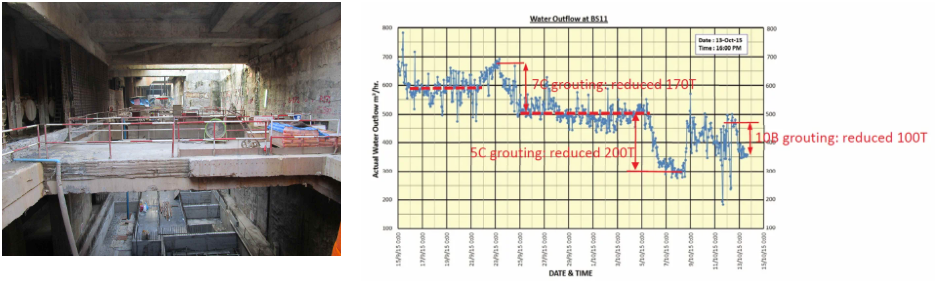
After the formulation of the plan, representative water outlets were selected for trial irrigation to confirm effective sealing. Upon successful confirmation, the grouting process was implemented at various locations with water seepage according to the construction design.
After completion of the phased work, the water discharge significantly decreased, allowing excavation to continue as per standards.
Due to the inability to execute comprehensive bottom sealing grouting, the Jines Construction Thailand branch team was on standby as per the contract to handle water inrush issues during the excavation process.
Upon successful completion of the excavation and bottom sealing of the underground station, the objectives of managing water seepage during subway station excavation and improving the site were successfully achieved.
—
Water Inrush Treatment and Ground Improvement at Thailand MRT Station Excavation
將下載檔案寄至:
・More Construction Result Sharing
Contact us:+886 2769-2355
Copyright ©Jines Construction Co.,Ltd